The mainboard, or motherboard, is the biggest and most important circuit board inside your computer. It's the home for all the important parts that make your computer work. Here are its main jobs:
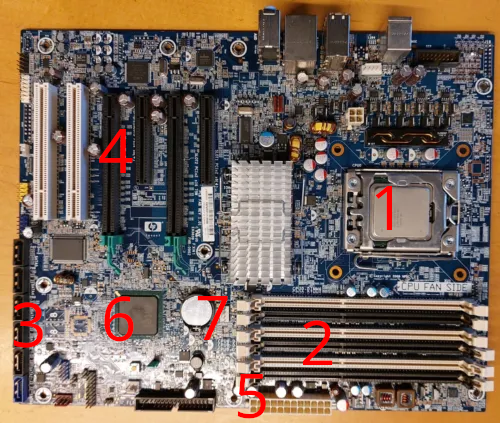
1: CPU Socket: This is where the computer's main chip, the CPU, goes. It's the spot where the computer's "brain" does all its thinking and figuring things out.
2: RAM Slots: Think of RAM as the computer's short-term memory. It helps your computer do many things at once. The more RAM capacity, the more things your computer can remember at the same time.
3: SATA Connectors: These are plugs for your computer's long-term memory (HDDs, SSDs, etc.), or physical disk drives.
4: PCie-Slots: These are extra rooms in your computer. You can add special cards, like graphics cards or Storage Connector expansion cards to these slots.
5: 24-Pin ATX Plug: This is where the Power Supply Unit is plugged in.
6: Chipset: The chipset on a mainboard is a component that helps different parts of the computer, like the CPU and peripherals, to communicate effectively. It manages data flow, ensuring everything works together smoothly for your computer to function properly.
7: BIOS battery: BIOS battery or CMOS battery, is a small, coin-shaped battery on the mainboard. It provides power to the CMOS memory, preserving critical system information such as date, time, and BIOS settings when the computer is powered off. If this battery weakens or fails, you may experience issues with system settings and need to replace it to maintain proper functionality.
RAM support
The mainboard's memory slots are specifically designed to support a certain type of RAM (e.g., DDR3, DDR4, DDR5). The chipset on the mainboard defines the maximum supported memory speed and capacity. The CPU must also support the type of RAM used. Modern CPUs are built to support specific memory types and speeds. For instance, some CPUs might support DDR4, but not DDR5, even if the mainboard has slots for both. The memory controller is built into modern CPUs, and it must match the type of RAM the mainboard is using.
For full compatibility, the mainboard, chipset and CPU need to align with the RAM type.
RAM channels
Dual-channel and quad-channel are memory configurations that enhance RAM performance by allowing multiple modules to work in parallel. Dual-channel uses two identical RAM sticks installed in matching slots, effectively x2 the data transfer rate. Quad-channel, on the other hand, requires four identical RAM sticks, increasing bandwidth and improving performance in memory-intensive tasks even further.
The CPU and mainboard work together to determine if a system can run in dual-channel or quad-channel memory configurations. While the mainboard chipset provides the necessary slots and support for these configurations, the CPU's memory controller controls how many channels it can support. Most mainstream CPUs (like Intel Core i5/i7 or AMD Ryzen) support dual-channel. High-end CPUs (like Intel Core i9 or AMD Threadripper) may support quad-channel or even octa-channel memory. In short: The CPU limits the number of channels, while the motherboard determines how they are physically configured.
